Recently Reserve bank of India has brought many of Public Sector Banks under prompt correction action (PCA) like Bank of India, Corporation bank, United Bank of India, UCO bank, Indian overseas bank, IDBI banks, Central Bank of India and lot more.
What is prompt correction action (PCA) and why RBI is implementing it on various banks ?
As per RBI definition ‘The PCA framework is intended to encourage banks to eschew certain riskier activities and focus on conserving capital so that their balance sheets can become stronger’.
It means The Prompt correction action or PCA is triggered when banks breach certain regulatory requirements like minimum capital, return on asset and quantum of non-performing assets. PCA is generally implemented to safeguard the bank from bankruptcy or any proposed merger. PCA helps bank in consolidating their balance book and improve profitability.
Read : Know The Financial Resolution and Deposit Insurance Bill (FRDI)
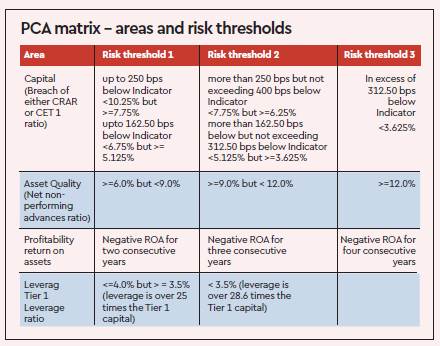
Reserve Bank of India measures bank on majorly three parameters like CRAR, Return on Assets (ROA) and Non Performing Assets (NPA). RBI has fixed certain benchmark in each of these category and bank’s are judged on these benchmarks.
What Will a Bank Do If PCA is Triggered ?
Once any of banks fall under PCA, it means such banks are not allowed to renew or accept costly deposits or take steps to increase their fee-based income.
Banks needs to check the existing Non Performing Assets (NPA) and speedy drive to further addition of any fresh NPAs. Banks are not allowed to enter in any new ventures or new lines of business. RBI will also impose restrictions on the bank on borrowings from inter-bank market.
Read : RBI levies Rs 2-5 crore penalty on Few Banks
Currently eight banks are imposed with PCA like Bank of India, Central Bank of India, UCO Bank, United Bank of India, IDBI Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, Corporation Bank etc.
Checkout RBI circular on Prompt Corrective Action (PCA)