Debt To Income Ratio For A Mortgage loan – you always pay your debt on time and your credit score is considerably high. You are very much sure about getting a home loan or mortgage loan from any banks, but not necessarily. Your loan application for mortgage may be rejected based on your debt to income ratio, or DTI.
DTI is a measure of your debt as it relates to your income. The ratio is more important than your credit score and is the main concern of lenders when considering whether to approve home loans or mortgage loan.
How does your Debt to Income Ratio measure up ?
DTI ratio tells lenders about your indebtedness. How much of your income goes toward paying debts and other related liabilities ? Before fixing the loan amount and further disbursement, the banks or lenders want to know that whether you’ll be able to make your mortgage payments on time or not. It has been seen that the borrowers with high Debt to income ratio are more likely to have trouble making those payments in long run.
How to Calculate Debt to Income Ratio ?
It’s easy to calculate Debt to Income Ratio, just follow the guidelines as mentioned below :
Step 1: Add Up All Of Your Monthly Debts
Your debt payments could include:
- Monthly rent or EMI on existing house payments
- Monthly child support payments or alimony
- Student loan payments
- Car payments
- Monthly credit card minimum payments
- Any other debts or EMI payment you might have
- Check your rating score with details to find out the major debts.
Note : You don’t need to add in:
- Grocery bills
- Utility bills
- Taxes
- Any other bills that may vary month to month
Sources of income can include:
- Wages
- Salaries
- Tips and bonuses
- Pension
- Social security
- Child support and alimony
Read – How To Calculate Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) ?
Step 2: Divide Your Monthly Debts (addition of Step-1) By Your Monthly Gross Income
For example, let’s say your debts add up to Rs 3,000 per month. If your monthly gross income (your before-tax income) is Rs 10,000 per month, then your DTI is 0.60, or 60%.
Another example to calculate DTI
Pretend you have a rent of Rs 1,000, a car payment of Rs 500, a minimum credit card payment of Rs 200 and a gross monthly income of Rs 5,000. Your debt-to-income ratio is Rs 1700 divided by Rs 5,000, which equals to 0.34 or 34%.
It’s important to note that the lower your Debt to Income Ratio, the less risky you are to lenders.
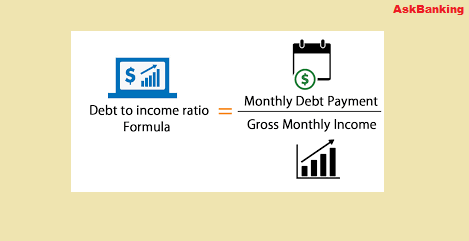
Formulae to calculate your DTI:
Different banks are having various guidelines as per the policy of their banks for sanctioning and granting Mortgage or housing based loan, but the calculation of DTI is same with all the banks whether it is private or public.
Read – How To Calculate Loan Installment to Income Ratio (IIR) ?
Good standards for Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio
Once you’ve calculated your DTI ratio, you’ll want to understand how lenders review it when they’re considering your loan application. Take a look at the guidelines majority of the lenders use:
35% or less: Looking Good – Relative to your income, your debt is at a manageable level.
You most likely have money left over for saving or spending after you’ve paid your bills. Lenders generally view a lower DTI as favorable.
36% to 49%: Opportunity to improve.
You’re managing your debt adequately, but you may want to consider lowering your DTI. This could put you in a better position to handle unforeseen expenses. If you’re looking to borrow, keep in mind that lenders may ask for additional eligibility criteria.
50% or more: Take Action – You may have limited funds to save or spend.
With more than half your income going toward debt payments, you may not have much money left to save, spend, or handle unforeseen expenses. With this DTI ratio, lenders may limit your borrowing options.